

Britannica Explains In these videos, Britannica explains a variety of topics and answers frequently asked questions.Britannica Classics Check out these retro videos from Encyclopedia Britannica’s archives.Miller, Computational Methods of Neutron Transport, American Nuclear Society, 1993, ISBN: 2-4. Hetrick, Dynamics of Nuclear Reactors, American Nuclear Society, 1993, ISBN: 3-2. Neuhold, Introductory Nuclear Reactor Dynamics, American Nuclear Society, 1985, ISBN: 9-4. Bezella, Introductory Nuclear Reactor Statics, American Nuclear Society, Revised edition (1989), 1989, ISBN: 3-2. Department of Energy, Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory. DOE Fundamentals Handbook, Volume 1 and 2. January 1993. Robert Reed Burn, Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Operation, 1988.Physics of Nuclear Kinetics. Addison-Wesley Pub. Nuclear and Particle Physics. Clarendon Press 1 edition, 1991, ISBN: 978-0198520467 Nuclear Reactor Engineering: Reactor Systems Engineering, Springer 4th edition, 1994, ISBN: 978-0412985317 Stacey, Nuclear Reactor Physics, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, ISBN: 0- 471-39127-1. Baratta, Introduction to Nuclear Engineering, 3d ed., Prentice-Hall, 2001, ISBN: 8-1. Lamarsh, Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Theory, 2nd ed., Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA (1983). This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom’s electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers.

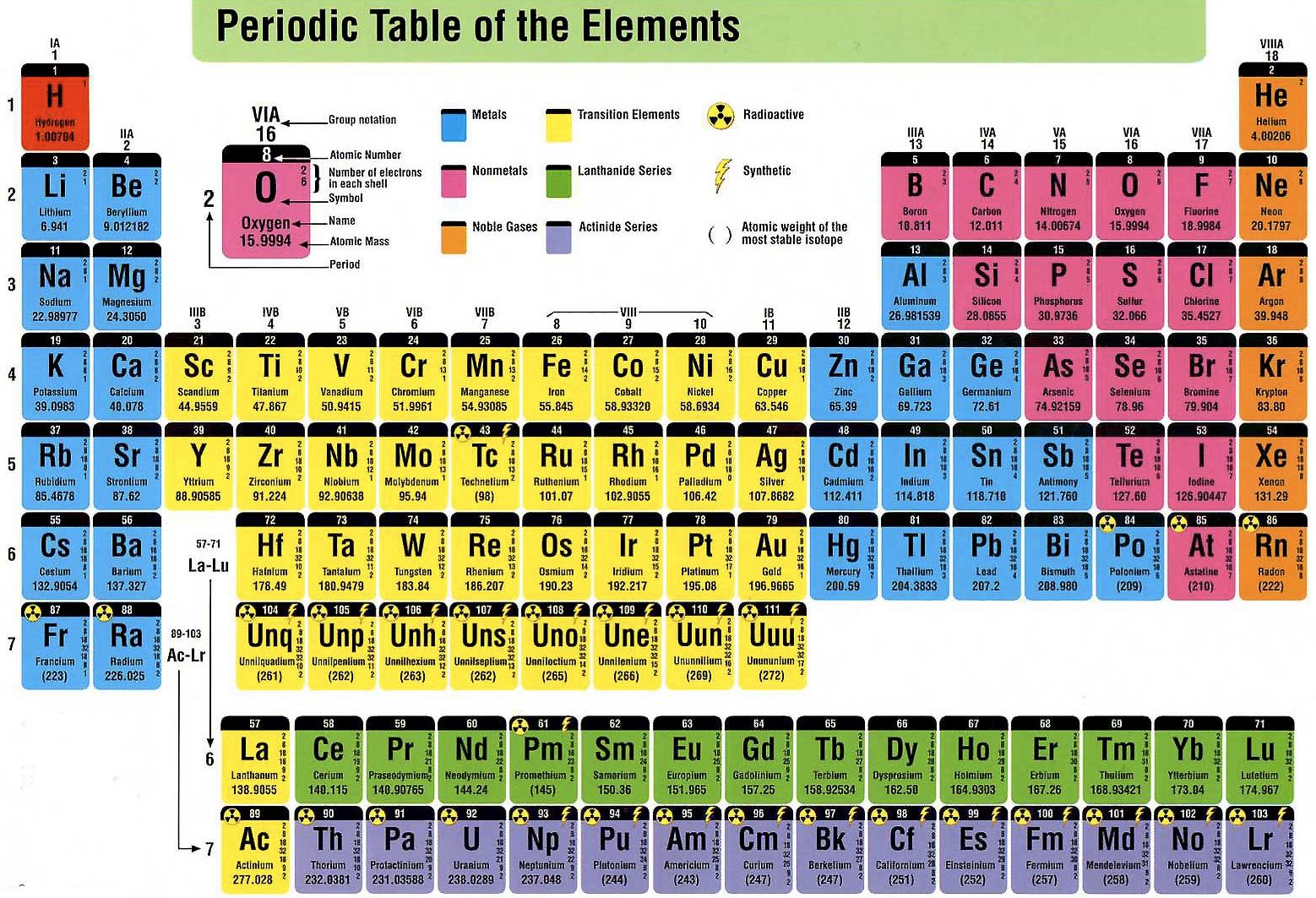
It is the Pauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. The total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number (or the proton number) of the atom and is given the symbol Z. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. There is a recurring pattern called the “periodic law” in their properties, in which elements in the same column (group) have similar properties. Generally, within one row (period) the elements are metals to the left, and non-metals to the right, with the elements having similar chemical behaviours placed in the same column.Įvery solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. It is organized in order of increasing atomic number. The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
